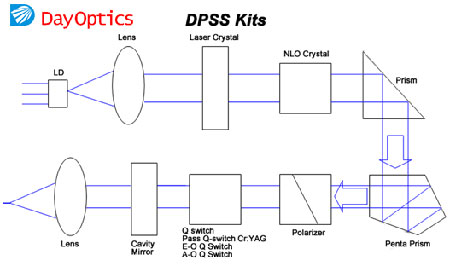
• Lens
Plano Convex Lens, Plano Concave Lens, Double Convex Lens , Double Concave Lens, Achromatic Lens, Cylindrical Lens
• Laser Crystal
Ti:Sapphire, Nd:YAG , Nd:YVO 4
• NLO Crystal
BBO, KTP , LBO, LiNbO 3
• Prism
Penta Prism, Beamsplitter Penta Prism, Right Angle Prism , Anamorphic Prism, Corner Cube Retroreflectors, Dove Prism
• Polarizer
Glan Taylor Polarizers, Glan Laser Polarizer, Glan Thompson Polarizers, Wollaston Polarizers, Rochon Polarizers
• E-O Switch
• A-O Switch
Solid State Lasers
The Solid State (SS) Laser uses a solid crystalline material as the lasing medium and is usually optically pumped. SS lasers should not be confused with semiconductor or diode lasers which are also 'solid state' but are almost always electrically pumped.
DPSS
Diode Pumped Solid State (DPSS) lasers are a variation of the well known ruby, Nd:YAG, or other type of optically pumped crystal based laser where a high power IR laser diode or array of laser diodes provides the excitation instead of a flashlamp or other intense light source. Note that many DPSS lasers are designed for SHG (Second Harmonic, 532 nm green for a YAG lasing medium) or higher frequency multiplication but this is not inherent in the DPSS designation.
Cavity Components
Like most other types of lasers, the heart of the solid state laser is the laser cavity or resonator. Properly selecting the cavity components and driving the pump source can make all the difference in terms of output pulse energy, beam quality, and stability.
Power Sources
High power laser diodes or arrays of laser diodes - Within the last 10 years, these have largely displaced arc lamps for most new CW SS lasers. A major reason is that the wall plug efficiency of a diode pumped laser can be many times better than for an arc lamp pumped laser since the wavelength of the laser diode and absorption band of the solid state lasing medium can be matched resulting in a transfer efficiency exceeding 50 percent.


